COMS 4995 Advanced Systems Programming
POSIX threads
Creating threads
Example: bank0.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h> // pthread_create, pthread_join
int balance = 0;
void* deposit(void *arg) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1e7; i++) {
++balance;
}
long r = 10 * (long)arg;
return (void *)r;
}
void* withdraw(void *arg) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1e7; i++) {
--balance;
}
long r = 10 * (long)arg;
return (void *)r;
}
int main() {
/* int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread,
const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine)(void *),
void *arg);
Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
pthread_t t1, t2;
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, &deposit, (void*)1);
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, &withdraw, (void*)2);
/* int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
void *r1;
void *r2;
pthread_join(t1, &r1);
pthread_join(t2, &r2);
printf("t1 returned %ld\n", (long)r1);
printf("t2 returned %ld\n", (long)r2);
printf("balance = %d\n", balance);
}
Processes vs. threads:
- Processes DO NOT share virtual memory address space
- Threads DO share virtual memory address space
- but each thread has its own stack
Thread synchronization problem:
-
i++is not an atomic operation: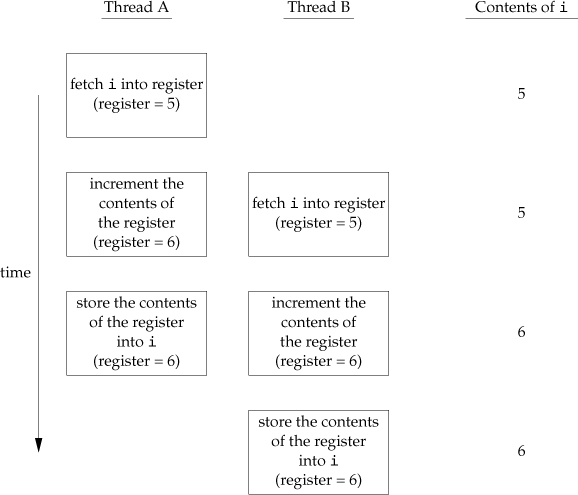
- We can use
objdump -dto inspect the assembly code of thebank0executable:$ objdump -d bank0 ... 00000000000011a9 <deposit>: 11a9: f3 0f 1e fa endbr64 11ad: 55 push %rbp 11ae: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp 11b1: 48 89 7d e8 mov %rdi,-0x18(%rbp) 11b5: c7 45 f4 00 00 00 00 movl $0x0,-0xc(%rbp) # int i = 0 11bc: eb 13 jmp 11d1 <deposit+0x28> # Jump to initial comparison 11be: 8b 05 50 2e 00 00 mov 0x2e50(%rip),%eax # balance -> %eax 11c4: 83 c0 01 add $0x1,%eax # Increment %eax 11c7: 89 05 47 2e 00 00 mov %eax,0x2e47(%rip) # %eax -> balance 11cd: 83 45 f4 01 addl $0x1,-0xc(%rbp) # i++ 11d1: 81 7d f4 7f 96 98 00 cmpl $0x98967f,-0xc(%rbp) # i < 1e7 11d8: 7e e4 jle 11be <deposit+0x15> # Jump to loop body if true 11da: 48 8b 55 e8 mov -0x18(%rbp),%rdx 11de: 48 89 d0 mov %rdx,%rax 11e1: 48 c1 e0 02 shl $0x2,%rax 11e5: 48 01 d0 add %rdx,%rax 11e8: 48 01 c0 add %rax,%rax 11eb: 48 89 45 f8 mov %rax,-0x8(%rbp) 11ef: 48 8b 45 f8 mov -0x8(%rbp),%rax 11f3: 5d pop %rbp 11f4: c3 ret ... - We can control the CPUs used by
bank0usingtaskset. CPU affinity is represented as a bitmask, with the least significant bit corresponding to the first logical CPU (i.e., processor #0). For example:taskset 3 bank0uses CPU #0 and CPU #1.taskset 1 bank0andtaskset 2 bank0use a single CPU, CPU #0 and CPU #1 respectively.
Even when using a single CPU, there is still a race condition. The thread can be interrupted and switched out in the middle of the three machine instructions for
balance++.
Mutex
Use a mutex lock to synchronize the threads (bank1.c):
int balance = 0;
pthread_mutex_t balance_lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void* deposit(void *arg) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1e7; i++) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&balance_lock);
++balance;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&balance_lock);
}
long r = 10 * (long)arg;
return (void *)r;
}
void* withdraw(void *arg) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1e7; i++) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&balance_lock);
--balance;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&balance_lock);
}
long r = 10 * (long)arg;
return (void *)r;
}
POSIX Mutex API:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
// Both return: 0 if OK, error number on failure
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
// All return: 0 if OK, error number on failure
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
int pthread_mutex_timedlock(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const struct timespec *restrict tsptr);
// Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure
Deadlock
-
Deadlock condition:
- A thread tries to lock the same mutex twice
- A Thread holds mutex A and tries to lock mutex B, and another thread holds mutex B and tries to lock mutex A
-
Strict lock ordering avoids deadlock
-
See APUE 11.11 and 11.12 for examples of using two mutexes
Condition variables
POSIX Condition Variables API:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
// Both return: 0 if OK, error number on failure
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const struct timespec *restrict tsptr);
// Both return: 0 if OK, error number on failure
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
// Both return: 0 if OK, error number on failure
Example from APUE 11.6.6:
#include <pthread.h>
struct msg {
struct msg *m_next;
/* ... more stuff here ... */
};
struct msg *workq;
pthread_cond_t qready = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
pthread_mutex_t qlock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void process_msg(void)
{
struct msg *mp;
for (;;) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&qlock);
while (workq == NULL)
pthread_cond_wait(&qready, &qlock);
mp = workq;
workq = mp->m_next;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&qlock);
/* now process the message mp */
}
}
void enqueue_msg(struct msg *mp)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&qlock);
mp->m_next = workq;
workq = mp;
pthread_cond_signal(&qready);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&qlock);
// In the textbook, the last two lines are written in reverse order:
//
// pthread_mutex_unlock(&qlock);
// pthread_cond_signal(&qready);
//
// Taking pthread_cond_signal() call out of the mutex region is
// allowed (and better) in this particular case, but it is not
// always safe to do so.
}
Condition Variables in Java:
-
Every class in Java extends
java.lang.Object - Each
java.lang.Objectcontains 1 mutex and 1 condition variable- Java class object is an example of a Monitor in OOP
-
synchronizedkeyword inserts mutex lock & unlock around a scopeclass account { int balance; public synchronized void deposit() { ++balance; } public synchronized void withdraw() { --balance; } } - See
wait(),notify()andnotifyAll()in java.lang.Object API
Last updated: 2024-02-11